KG embedding algorithms
- Before discussing individual algorithms, we will go through some high-level generalization of the embedding techniques which make each algorithm unique. This will help us differentiate and hence appreciate the individual algorithms.
Generalization of embedding methods
- Embedding is the way of representing an object from its existing environment to another.
- Knowledge graph embedding includes representation of relations and entities into continuous space.
- Models for KG embedding can be categorised based on their answer for following questions, (Ji_2021)
- What is the representation space in which the relations and entities are represented?
- What is the scoring function for measuring the plausibility of factual triples?
Representation space
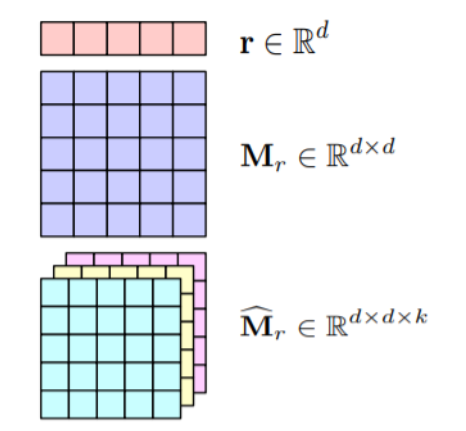
Point-wise Euclidean space
- The most common representation space.
- Embedding space is Euclidean real valued vector or matrix space.
- Easy to understand; Not ideal for graphical (tree-like) structure.
Complex vector space
- Entities and relations are represented in a complex space
- Taking head entity as an example, h has a real part Re(h) and an imaginary part Im(h), i.e., \(\textbf{h}=Re(\textbf{h}) + i Im(\textbf{h})\)
- Can capture anti-symmetric relations better than operations in Euclidean space.
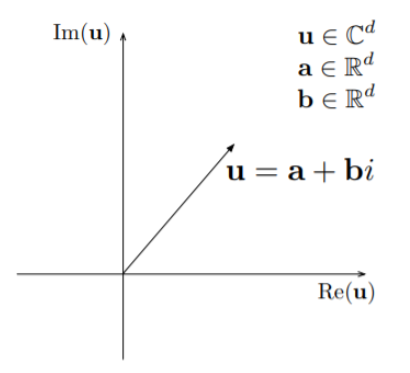
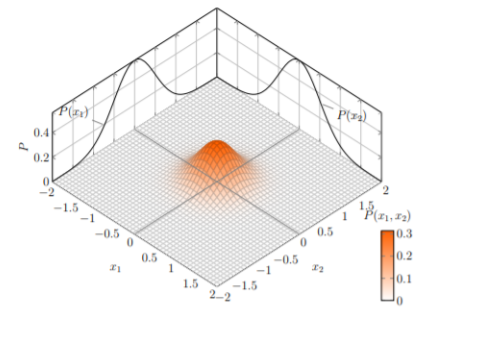
Gaussian distribution space
- Entities and relations are represented as probabilistic distribution
- Applicable if you want to capture uncertainties.
Manifold space
- Entities and relations are represented in a well defined topological space
- Good for graphical (tree-like) structure.
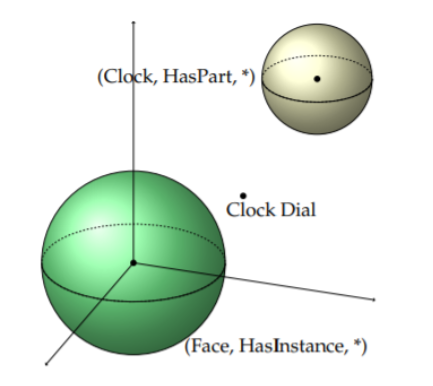
Scoring functions
Distance based
- Measure plausibility of facts by calculating the distance between the entities.
- Additive translation with relation is the most widely used method i.e. \(\textbf{h} + \textbf{r} \approx \textbf{t}\)
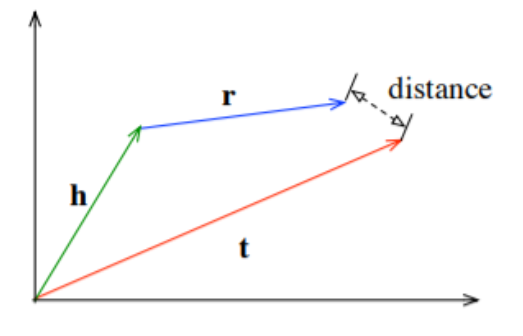
Similarity based
- Measure plausibility of the facts by semantic similarity matching
- Multiplicative formulation is most widely used method i.e. \(\textbf{h}^T \textbf{M}_r \approx \textbf{t}^T\) , use relation matrix to transform head entity into tail entity.
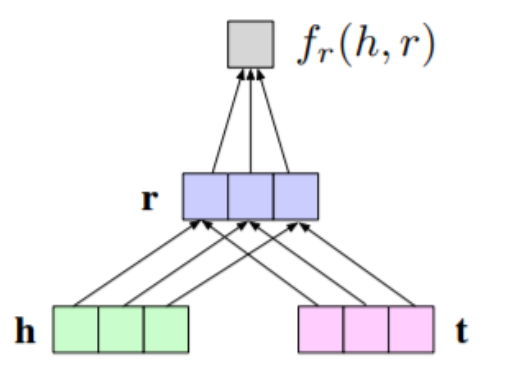
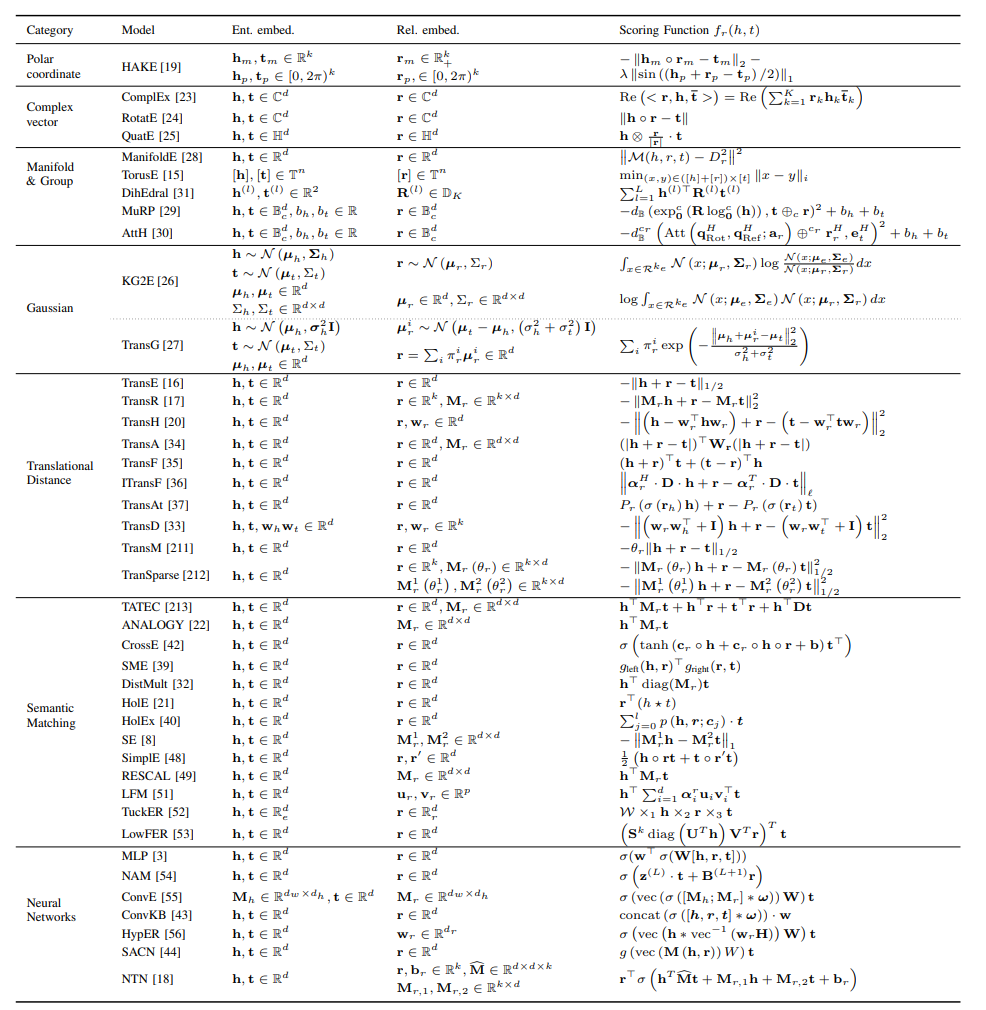
Algorithm Comparison
- A holistic comparison of different knowledge graph emebdding techniques w.r.t. category and scoring function is provided below,